Embark on a scientific odyssey with our comprehensive Atoms and Elements Webquest Answer Key, a treasure trove of knowledge that unlocks the fundamental principles governing the microscopic world. Delve into the intricate structure of atoms, unravel the secrets of the periodic table, and explore the fascinating properties and applications of elements that shape our universe.
As we navigate this captivating journey, we’ll decipher the enigmatic nature of atoms, their constituent particles, and the forces that bind them together. The periodic table, a roadmap of the elements, will reveal the patterns and trends that govern their behavior.
We’ll delve into the diverse properties of elements, from their physical characteristics to their chemical reactivity, and uncover how these properties underpin the countless applications that enrich our lives.
Introduction to Atoms and Elements
Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of matter. They are composed of three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus of the atom, while electrons orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels.
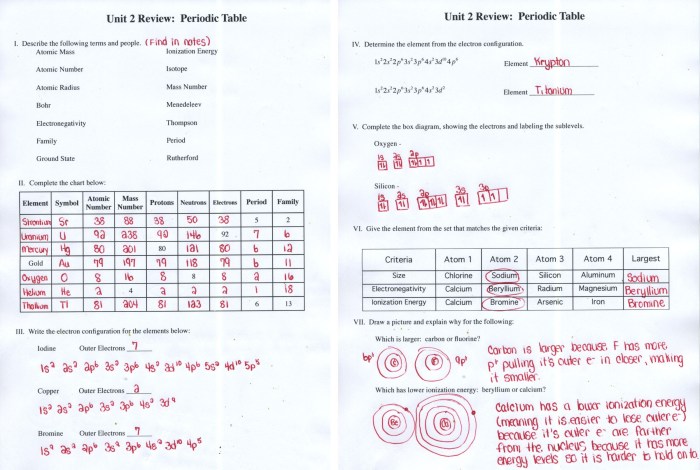
The atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. The mass number of an atom is equal to the total number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus.
Periodic Table of Elements, Atoms and elements webquest answer key
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, organized on the basis of their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties.
The periodic table is divided into 18 vertical columns, called groups, and 7 horizontal rows, called periods. The elements in a group have similar chemical properties, while the elements in a period have the same number of electron shells.
- Alkali metals (Group 1): Highly reactive, form 1+ ions
- Halogens (Group 17): Highly reactive, form 1- ions
- Noble gases (Group 18): Unreactive, do not form ions
Properties of Elements
The properties of elements are determined by their atomic structure. For example, the number of valence electrons in an atom determines its chemical reactivity.
- Metals: Shiny, malleable, ductile, good conductors of heat and electricity
- Nonmetals: Dull, brittle, poor conductors of heat and electricity
- Metalloids: Properties intermediate between metals and nonmetals
Element Compounds
Elements can combine with each other to form compounds. Compounds are held together by chemical bonds, which are forces that attract atoms to each other.
There are two main types of chemical bonds: ionic bonds and covalent bonds.
- Ionic bonds: Formed between atoms that have opposite charges
- Covalent bonds: Formed between atoms that share electrons
Applications of Elements
Elements are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Medicine: Elements are used in the production of drugs, vaccines, and medical devices.
- Technology: Elements are used in the production of computers, cell phones, and other electronic devices.
- Energy: Elements are used in the production of fossil fuels, nuclear energy, and renewable energy sources.
Query Resolution: Atoms And Elements Webquest Answer Key
What is the smallest unit of an element?
An atom
What is the name of the table that organizes elements based on their properties?
Periodic table
What is the difference between an atom and an ion?
An ion is an atom that has gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net electrical charge.