Food chains food webs and ecological pyramids worksheet answers – Embark on an educational journey with our comprehensive worksheet answers for food chains, food webs, and ecological pyramids. Dive into the intricacies of these fundamental ecological concepts, unraveling their significance in maintaining ecosystem equilibrium and understanding the delicate balance of nature.
From the foundational principles of food chains to the intricate dynamics of food webs, this exploration unravels the complexities of ecological pyramids, empowering you with a deeper comprehension of ecological systems.
Food Chains
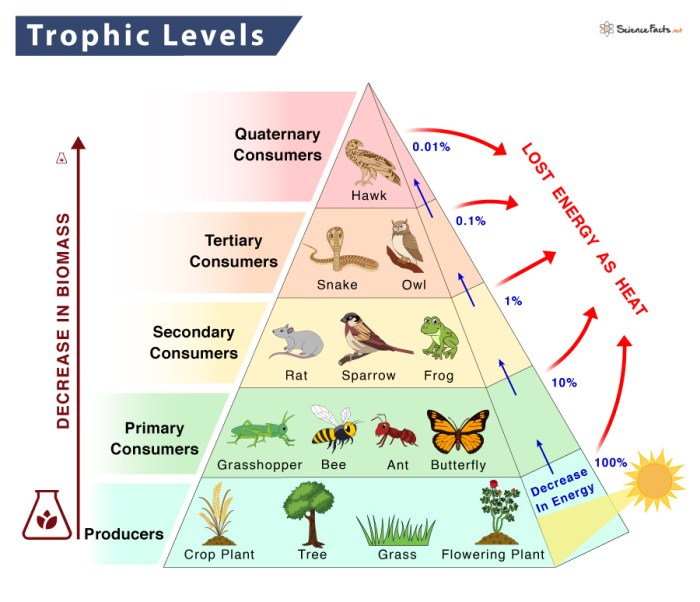
Food chains represent the linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass within an ecosystem. Each organism in the chain consumes the one below it and is consumed by the one above it. Understanding food chains helps ecologists comprehend the flow of energy and the interconnectedness of species in an ecosystem.
Examples of Food Chains:
- Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk
- Phytoplankton → Zooplankton → Small Fish → Large Fish → Shark
- Plants → Deer → Lion → Hyena
Role of Producers, Consumers, and Decomposers:
- Producers (Autotrophs):Organisms that create their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis.
- Consumers (Heterotrophs):Organisms that rely on other organisms for food.
- Decomposers:Organisms that break down dead organisms and return nutrients to the ecosystem.
Food Webs: Food Chains Food Webs And Ecological Pyramids Worksheet Answers
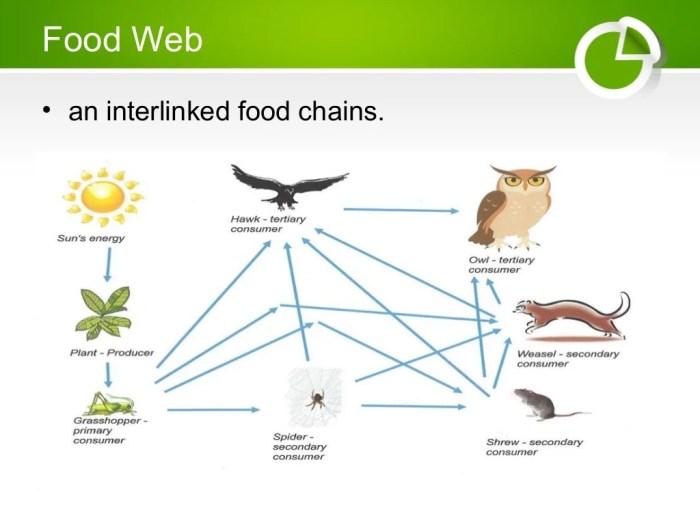
Food webs are complex networks of interconnected food chains within an ecosystem. They provide a more comprehensive representation of the feeding relationships among species. Unlike food chains, food webs acknowledge the multiple trophic levels and interconnectedness of organisms.
Diagram of a Food Web:
[Diagram yang menunjukkan berbagai spesies yang saling berhubungan dalam food web, dengan panah yang menunjukkan arah aliran energi]
Importance of Food Webs:
- Provide stability to ecosystems by maintaining species diversity.
- Facilitate energy flow and nutrient cycling.
- Help predict the impact of environmental changes on species populations.
Ecological Pyramids
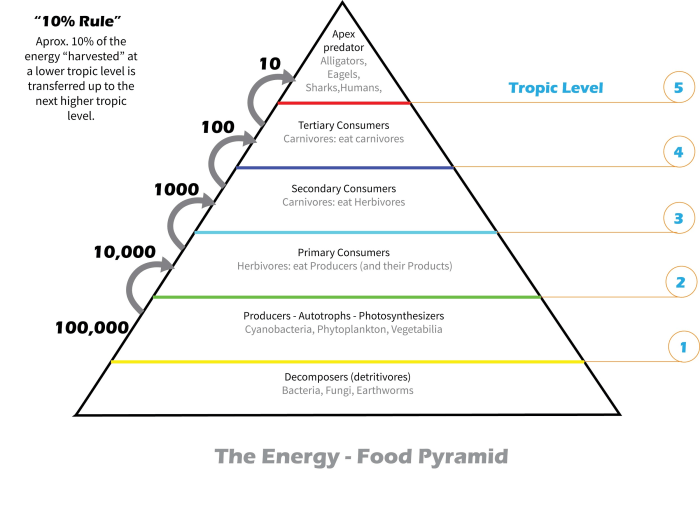
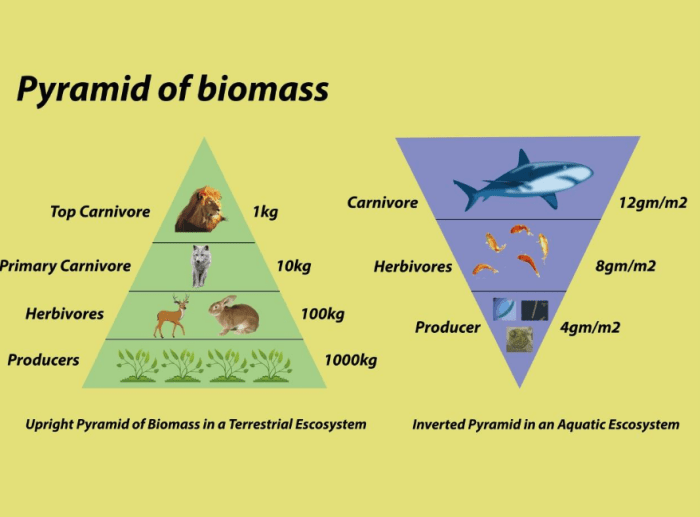
Ecological pyramids are graphical representations that depict the distribution of energy, biomass, or numbers within an ecosystem. They illustrate the trophic levels and the relative abundance of organisms at each level.
Types of Ecological Pyramids:
- Pyramid of Numbers:Represents the number of organisms at each trophic level.
- Pyramid of Biomass:Represents the total mass of organisms at each trophic level.
- Pyramid of Energy:Represents the amount of energy available at each trophic level.
Example of Constructing an Ecological Pyramid:
[Diagram yang menunjukkan sebuah piramida ekologi dengan tingkat trofik di sepanjang sumbu x dan nilai numerik di sepanjang sumbu y]
Limitations and Applications of Ecological Pyramids:
- Limitations:May not account for seasonal variations, species interactions, or energy loss.
- Applications:Useful for comparing ecosystems, assessing ecosystem health, and predicting population dynamics.
Key Questions Answered
What is the primary difference between a food chain and a food web?
A food chain represents a linear sequence of energy transfer, while a food web depicts the interconnected feeding relationships within an ecosystem, involving multiple paths of energy flow.
How do ecological pyramids illustrate ecological relationships?
Ecological pyramids graphically represent the abundance or biomass of organisms at different trophic levels, providing insights into energy flow and ecological stability.
What role do decomposers play in food chains and food webs?
Decomposers break down dead organisms and organic matter, returning nutrients to the ecosystem and facilitating the recycling of energy.