Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells pogil answers unravel the intricate differences between the fundamental building blocks of life. Dive into the captivating world of cellular biology as we explore the defining characteristics, functions, and evolutionary implications that set these two cell types apart.
Prokaryotic cells, the simpler and more ancient of the two, lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, possess a complex internal organization, including a nucleus, mitochondria, and other specialized structures. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for comprehending the diversity and complexity of life on Earth.
Introduction
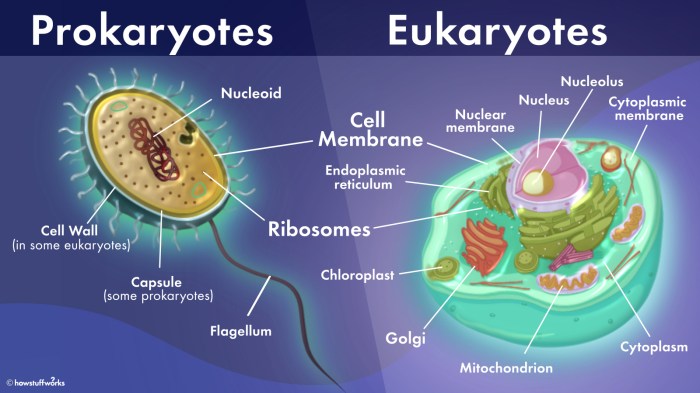
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are the two main types of cells that exist in living organisms. They differ significantly in their structure, function, and complexity. Understanding these differences is crucial for comprehending the diversity of life on Earth and the evolutionary history of cells.
Prokaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic cells are the simplest and most ancient type of cells. They are typically small, ranging from 0.1 to 5 micrometers in diameter, and lack a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotic cells have a single, circular chromosome that is located in the cytoplasm.
They also have ribosomes, which are responsible for protein synthesis.
Prokaryotic cells are found in a wide variety of habitats, including soil, water, and the human body. They are the most abundant type of cell on Earth, and they play an essential role in the cycling of nutrients and the decomposition of organic matter.
Eukaryotic Cells
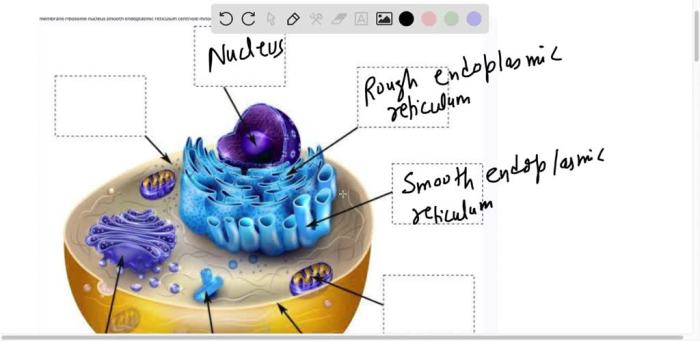
Eukaryotic cells are more complex than prokaryotic cells. They are typically larger, ranging from 10 to 100 micrometers in diameter, and have a nucleus that is surrounded by a nuclear membrane. Eukaryotic cells also have a variety of membrane-bound organelles, including mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus.
These organelles perform specialized functions that are essential for the cell’s survival.
Eukaryotic cells are found in all multicellular organisms, including plants, animals, and fungi. They are also found in some single-celled organisms, such as yeast and protozoa.
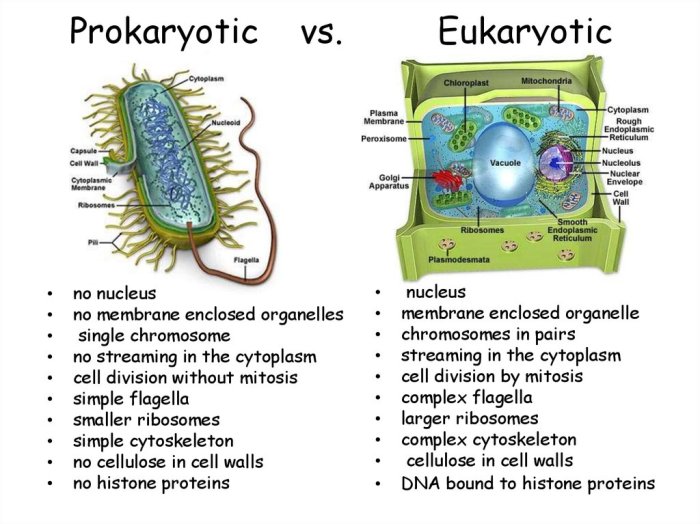
Comparison of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
| Characteristic | Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Size | 0.1-5 micrometers | 10-100 micrometers |
| Nucleus | Absent | Present |
| Membrane-bound organelles | Absent | Present |
| Cell division | Binary fission | Mitosis or meiosis |
General Inquiries: Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells Pogil Answers
What is the primary difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
The presence of a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles is the key distinction.
What are the characteristic features of prokaryotic cells?
Prokaryotes are typically smaller, lack a nucleus, and have a simpler internal organization.
How do eukaryotic cells differ from prokaryotic cells in terms of complexity?
Eukaryotic cells are more complex, with a nucleus, mitochondria, and other membrane-bound organelles.