Active and passive transport worksheet answers – Embarking on a journey into the realm of active and passive transport, this comprehensive guide unveils the answers to your burning questions, unraveling the intricate processes that govern the movement of molecules across cell membranes. Dive into the depths of this worksheet, and emerge with a profound understanding of these fundamental biological mechanisms.
Delving into the complexities of active and passive transport, we will explore the pivotal role of proteins in facilitating molecular movement, unravel the diverse types of passive transport, and unveil the intricate interplay between these processes in maintaining cellular homeostasis.
Active and Passive Transport: Active And Passive Transport Worksheet Answers
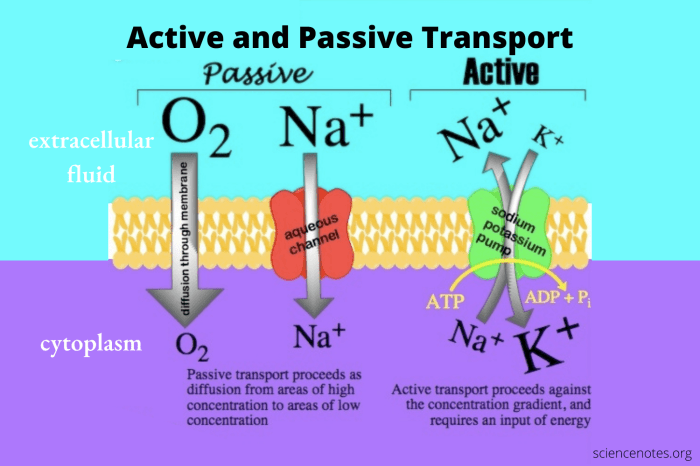
Cells require the movement of molecules across their membranes to maintain homeostasis. Active and passive transport are two distinct processes that facilitate this movement. Active transport moves molecules against their concentration gradient, requiring energy input, while passive transport moves molecules down their concentration gradient, requiring no energy input.
Active Transport
Active transport is the movement of molecules from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. This process requires energy, which is typically provided by adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Integral membrane proteins, known as pumps or carriers, facilitate active transport.
These proteins bind to molecules and use energy to move them across the membrane.
- Sodium-potassium pump:Transports sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell, maintaining the electrochemical gradient across the membrane.
- Calcium pump:Removes calcium ions from the cytoplasm, regulating calcium levels and preventing cellular damage.
- Hydrogen pump:Pumps hydrogen ions out of the cell, creating a proton gradient used for ATP synthesis and other cellular processes.
Passive Transport
Passive transport is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. This process does not require energy input. There are several types of passive transport:
- Simple diffusion:Molecules move directly across the lipid bilayer of the membrane.
- Facilitated diffusion:Molecules move across the membrane with the assistance of membrane proteins.
- Osmosis:Water moves across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
- Oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange in the lungs:Oxygen diffuses into the blood from the lungs, while carbon dioxide diffuses out.
- Nutrient absorption in the small intestine:Nutrients diffuse from the small intestine into the bloodstream.
- Water absorption in the kidneys:Water moves from the renal tubules into the bloodstream.
Comparison of Active and Passive Transport, Active and passive transport worksheet answers
| Characteristic | Active Transport | Passive Transport |
|---|---|---|
| Energy required | Yes | No |
| Direction of movement | Against concentration gradient | Down concentration gradient |
| Mechanism | Membrane proteins (pumps or carriers) | Diffusion or facilitated diffusion |
| Examples | Sodium-potassium pump, calcium pump | Simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis |
Active and passive transport work together to maintain homeostasis. Active transport establishes and maintains concentration gradients, while passive transport utilizes these gradients to move molecules into or out of cells. These processes are essential for cellular function and overall organismal health.
Applications of Active and Passive Transport
- Medicine:Active transport is used in drug delivery systems to target specific tissues or cells. Passive transport is used in drug absorption and distribution.
- Environmental science:Active transport is involved in the uptake of nutrients by plants and the detoxification of pollutants. Passive transport is involved in the movement of water and pollutants through soil and groundwater.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the primary difference between active and passive transport?
Active transport requires energy to move molecules against a concentration gradient, while passive transport does not.
Name the three main types of passive transport.
Diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion.
How does active transport contribute to maintaining cellular homeostasis?
By regulating the concentration of ions and molecules within the cell, active transport helps maintain the cell’s internal environment.