Geotour worksheet f sedimentary rocks – Introducing the Geotour Worksheet for Sedimentary Rocks, an immersive educational tool designed to transform field experiences into captivating learning journeys. This worksheet empowers students to engage with the fascinating world of sedimentary rocks, fostering a deep understanding of their formation, classification, and significance.
Through a series of interactive activities, students embark on a hands-on exploration of sedimentary rocks, honing their observational skills, data collection techniques, and analytical abilities. The worksheet’s logical structure and clear instructions guide them seamlessly through the exploration process, ensuring a comprehensive and engaging learning experience.
Introduction
A geotour worksheet for sedimentary rocks is a valuable educational tool designed to enhance the learning experience during a geological field trip or classroom session.
It provides a structured framework for students to observe, analyze, and interpret the characteristics of sedimentary rocks, fostering a deeper understanding of their formation, composition, and significance.
Target Audience and Learning Objectives
This worksheet is primarily intended for students in introductory geology or Earth science courses. Its learning objectives include:
- Identifying and classifying different types of sedimentary rocks based on their texture, composition, and depositional environment.
- Understanding the processes involved in the formation of sedimentary rocks, including erosion, transportation, deposition, and lithification.
- Developing critical thinking skills through observation, analysis, and interpretation of geological data.
li>Interpreting sedimentary structures and fossils to infer the depositional environment and geological history of the area.
Geological Background
Sedimentary rocks form when sediments, such as sand, mud, and organic matter, are deposited and compacted over time. These sediments can come from various sources, including the weathering of existing rocks, the erosion of soil, and the accumulation of organic matter from plants and animals.
Sedimentary rocks are classified based on their texture, composition, and depositional environment. Texture refers to the size and shape of the grains that make up the rock, while composition refers to the mineral content. Depositional environment refers to the conditions under which the sediments were deposited, such as in a river, lake, or ocean.
Grain Size
The grain size of a sedimentary rock is one of its most important characteristics. Grain size can range from very fine-grained (less than 0.0625 mm) to very coarse-grained (greater than 2 mm). The grain size of a rock is determined by the size of the particles that make up the rock and the amount of compaction that the rock has undergone.
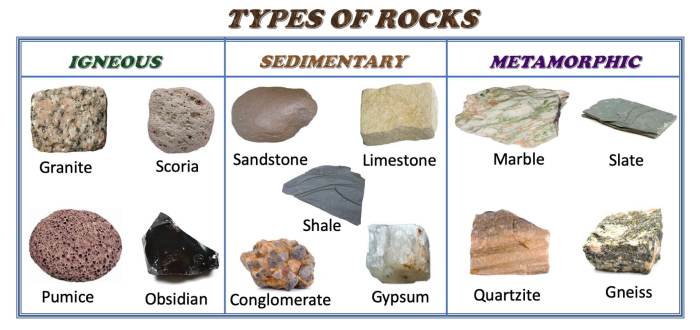
- Conglomerate:A sedimentary rock composed of rounded pebbles or cobbles.
- Sandstone:A sedimentary rock composed of sand-sized grains.
- Shale:A sedimentary rock composed of clay-sized particles.
Composition
The composition of a sedimentary rock is another important characteristic. Sedimentary rocks can be composed of a variety of minerals, including quartz, feldspar, calcite, and clay minerals. The composition of a rock is determined by the minerals that were present in the sediments that formed the rock.
- Limestone:A sedimentary rock composed primarily of calcite.
- Dolomite:A sedimentary rock composed primarily of dolomite.
- Chert:A sedimentary rock composed primarily of silica.
Depositional Environment
The depositional environment of a sedimentary rock is another important characteristic. Sedimentary rocks can be deposited in a variety of environments, including rivers, lakes, oceans, and deserts. The depositional environment of a rock is determined by the conditions under which the sediments were deposited.
- Fluvial:A sedimentary rock that was deposited in a river.
- Lacustrine:A sedimentary rock that was deposited in a lake.
- Marine:A sedimentary rock that was deposited in an ocean.
- Aeolian:A sedimentary rock that was deposited by the wind.
Geotour Activities
The geotour incorporates interactive activities that engage students with sedimentary rocks in the field. These activities foster observation, data collection, and interpretation skills, enhancing their understanding of sedimentary processes and environments.
The activities are designed to be hands-on and engaging, promoting active learning and a deeper appreciation for the geological significance of sedimentary rocks.
Rock Identification and Classification
- Students examine various sedimentary rock samples and use identification keys to determine their type and composition.
- They record their observations, including grain size, texture, color, and any visible fossils or minerals.
- Based on their observations, students classify the rocks into different categories, such as sandstone, limestone, or shale.
Sedimentary Structures Analysis
- Students observe sedimentary structures within the rock outcrops, such as bedding planes, cross-bedding, or ripple marks.
- They document the orientation, size, and shape of these structures, which provide clues about the depositional environment.
- By interpreting the sedimentary structures, students can infer the direction of water flow, the energy of the depositional system, and the presence of ancient currents or tides.
Paleontological Investigations
- Students search for fossils within the sedimentary rocks and identify them based on their shape, size, and morphology.
- They record the type and abundance of fossils, which can provide insights into the ancient environment and the organisms that inhabited it.
- By analyzing the fossil record, students can reconstruct past ecosystems, understand the evolution of life, and explore the relationships between organisms and their environment.
Worksheet Structure
To facilitate effective use and understanding, the worksheet is organized into logical sections:
Introduction
This section provides an overview of the geotour, its purpose, and the objectives of the activities.
Activities, Geotour worksheet f sedimentary rocks
The activities section comprises a series of guided exercises designed to engage students with the sedimentary rocks and geological features at the site. Each activity is clearly Artikeld with:
- A concise title
- Step-by-step instructions
- Guiding questions or tasks
- Data tables or other templates for recording observations and data
Data Tables
The worksheet includes data tables for students to record their observations and measurements during the activities. These tables are designed to facilitate data analysis and interpretation.
Conclusion
The conclusion section provides a space for students to summarize their findings, reflect on their learning, and connect the geotour experience to broader geological concepts.
Data Analysis
After collecting data during the geotour, students should analyze and interpret it to understand the sedimentary rocks they encountered.
One method for identifying and classifying sedimentary rocks is to examine their texture, composition, and sedimentary structures.
Texture
- Texture refers to the size, shape, and arrangement of the grains in a sedimentary rock.
- Common textures include clastic (composed of broken fragments of other rocks or minerals), chemical (formed by the precipitation of minerals from solution), and organic (formed from the remains of plants or animals).
Composition
- Composition refers to the mineral content of a sedimentary rock.
- Common compositions include sandstone (composed primarily of quartz), limestone (composed primarily of calcite), and shale (composed primarily of clay minerals).
Sedimentary Structures
- Sedimentary structures are features that form during the deposition and lithification of sediments.
- Common sedimentary structures include bedding (layers of sediment), cross-bedding (layers of sediment that are inclined to the main bedding), and ripple marks (small, wave-like features on the surface of a sedimentary rock).
Assessment

Assessing student learning is crucial to evaluate their understanding of sedimentary rock concepts and their ability to apply this knowledge in the field. To effectively assess student learning, incorporate a variety of assessment strategies, such as:
- Observation of student participation during geotour activities:Observe students’ engagement, questions, and discussions to gauge their comprehension and enthusiasm.
- Review of student worksheets:Evaluate students’ responses to questions and tasks to assess their understanding of sedimentary rock characteristics, depositional environments, and geologic time.
- Field-based quizzes or short answer questions:Administer quizzes during or after the geotour to test students’ ability to identify and interpret sedimentary rock features in the field.
- Group presentations or projects:Assign students to prepare presentations or projects that showcase their understanding of sedimentary rock concepts and their significance in understanding Earth’s history.
Student Learning Outcomes
These assessment strategies should align with specific student learning outcomes, such as:
- Students can identify and describe different types of sedimentary rocks based on their texture, composition, and depositional environments.
- Students can interpret sedimentary structures and fossils to infer past environmental conditions and geologic processes.
- Students can apply their knowledge of sedimentary rocks to reconstruct Earth’s history and understand the processes that shape our planet.
Resources: Geotour Worksheet F Sedimentary Rocks
In addition to the materials provided in this geotour worksheet, students are encouraged to explore the following resources for further understanding of sedimentary rocks:
Websites:
Books:
- Sedimentary Rocksby Doris M. Curtis
- Sedimentary Geologyby Donald R. Prothero and Fred Schwab
- The Sedimentary Rock Recordby Paul A. Scholle and Don L. Gautier
Articles:
- The Role of Sedimentary Rocks in the Carbon Cycle
- Unraveling the History of Life on Earth from Sedimentary Rocks
- Sedimentary Rocks as Indicators of Past Climate Change
Questions and Answers
What is the purpose of the Geotour Worksheet for Sedimentary Rocks?
The worksheet serves as a comprehensive guide for students to engage with sedimentary rocks in the field, fostering an in-depth understanding of their formation, classification, and significance.
Who is the target audience for this worksheet?
The worksheet is designed for students interested in Earth science, particularly those studying sedimentary rocks. It is suitable for use in high school and undergraduate geology courses.
How does the worksheet promote student engagement?
The worksheet incorporates interactive activities, data collection exercises, and analytical tasks that actively engage students in the learning process, fostering a deeper understanding of sedimentary rocks.