Lewin’s Change Theory in Nursing PPT offers a comprehensive framework for understanding and implementing change within the healthcare setting. Developed by Kurt Lewin, this theory provides a structured approach to guide nurses in navigating the challenges and opportunities associated with change initiatives.
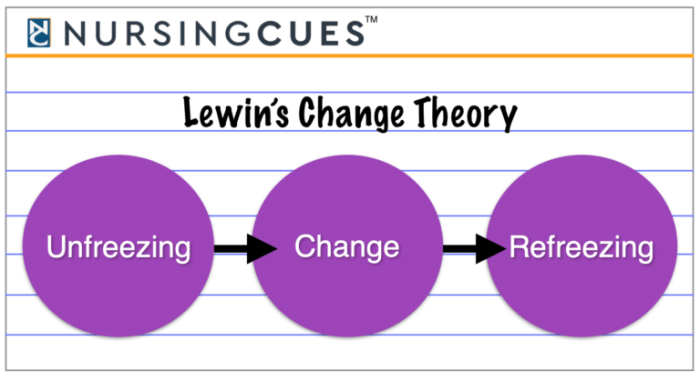
The theory consists of three distinct stages: unfreezing, changing, and refreezing. Each stage involves specific strategies and techniques that nurses can employ to effectively manage change and achieve desired outcomes.
Introduction
Lewin’s Change Theory is a widely accepted model that explains the process of individual and organizational change. Developed by psychologist Kurt Lewin in the 1940s, this theory provides a framework for understanding the dynamics of change and how to manage it effectively.
Lewin’s theory is particularly relevant to nursing practice, as nurses are often involved in facilitating change within healthcare organizations and patient care. Understanding the principles of this theory can help nurses plan, implement, and evaluate change initiatives more effectively.
Lewin’s Three-Step Model
Lewin’s Change Theory is based on a three-step model: unfreezing, changing, and refreezing. Each step represents a distinct phase in the change process:
- Unfreezing:This phase involves preparing individuals or organizations for change by creating a sense of urgency and motivation. It includes identifying the need for change, communicating the rationale, and addressing any resistance.
- Changing:During this phase, the actual change is implemented. This may involve introducing new policies, procedures, or technologies, or modifying existing ones. It is important to provide support and guidance to individuals throughout this phase to ensure a smooth transition.
- Refreezing:This final phase involves stabilizing the change and making it a permanent part of the organization or individual’s behavior. It includes reinforcing the new behaviors, evaluating the outcomes, and making any necessary adjustments to ensure sustainability.
Stages of Change

Lewin’s Change Theory is a widely recognized and influential model in nursing, encompassing three distinct stages: unfreezing, changing, and refreezing. This structured approach guides nurses in implementing and sustaining meaningful change within healthcare settings.
Unfreezing
The unfreezing stage involves preparing individuals for change by challenging existing attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors. Nurses play a crucial role in creating a sense of urgency and dissatisfaction with the current state, fostering a readiness for change. Unfreezing Strategies in Nursing
- Assessing organizational culture and identifying barriers to change
- Providing education and training to increase awareness of the need for change
- Creating a sense of urgency by highlighting potential consequences of inaction
- Encouraging open dialogue and feedback to address concerns and resistance
Factors Influencing Change
Change in nursing is influenced by a complex interplay of internal and external factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for effective change management and implementation.
Internal Factors
Internal factors are those that reside within the individual nurse or nursing team. They include:
Knowledge and skills
Nurses’ knowledge and skills directly impact their ability to adapt to change. Lack of knowledge or skills can create barriers to change.
Attitudes and beliefs
Nurses’ attitudes and beliefs about change can influence their willingness to embrace it. Negative attitudes or beliefs can hinder change efforts.
Perceived self-efficacy
Nurses’ confidence in their ability to successfully implement change influences their willingness to engage in it. Low self-efficacy can be a barrier to change.
Motivation
Nurses’ motivation to change is driven by factors such as perceived benefits, job satisfaction, and professional growth. Lack of motivation can impede change efforts.
Addressing Internal Barriers to Change
To address internal barriers to change, nurse leaders can:
- Provide training and education to enhance knowledge and skills.
- Foster a positive change culture that encourages open communication and collaboration.
- Build nurses’ self-efficacy through supportive supervision and recognition.
- Create incentives and rewards to motivate nurses to embrace change.
External Factors
External factors are those that exist outside the individual nurse or nursing team and can influence change efforts. They include:
Organizational culture
The culture of the healthcare organization can significantly impact change initiatives. A rigid or bureaucratic culture can hinder change, while a flexible and innovative culture can facilitate it.
Leadership
Strong leadership is essential for successful change management. Effective leaders can inspire and motivate nurses to embrace change, provide clear direction, and remove barriers.
Resources
Adequate resources, such as funding, equipment, and personnel, are crucial for implementing change effectively. Lack of resources can hinder change efforts.
External regulations
Changes in healthcare regulations can necessitate changes in nursing practice. Nurses must be aware of and adapt to these external regulations.
Strategies for Overcoming External Barriers to Change
To overcome external barriers to change, nurse leaders can:
- Influence organizational culture through advocacy and collaboration.
- Build strong relationships with leaders to gain support and resources.
- Secure adequate funding and resources through strategic planning and resource allocation.
- Monitor and adapt to changes in external regulations through ongoing professional development.
Applications in Nursing: Lewin’s Change Theory In Nursing Ppt
Lewin’s Change Theory has found extensive applications in nursing practice, guiding nurses in effectively implementing and managing change within healthcare organizations and patient care settings.
Nurses play a crucial role in facilitating and supporting change, as they are often the frontline providers of care and have direct contact with patients and their families. Lewin’s theory provides a structured framework for nurses to understand and navigate the change process, empowering them to drive positive outcomes for patients, organizations, and the healthcare system as a whole.
Case Studies
Numerous case studies have demonstrated the successful application of Lewin’s Change Theory in nursing practice.
- Implementation of a new electronic health record (EHR) system:Nurses used Lewin’s model to guide the implementation of a new EHR system, involving stakeholders in the planning, implementation, and evaluation phases. The use of the model ensured a smooth transition, minimized resistance, and promoted adoption of the new system.
- Introduction of a new patient care protocol:A nursing team employed Lewin’s theory to introduce a new patient care protocol for managing chronic conditions. By involving patients and families in the change process, building consensus, and providing ongoing support, the team successfully implemented the protocol, leading to improved patient outcomes.
- Redesign of a hospital unit:A hospital unit underwent a redesign to improve patient flow and efficiency. Nurses applied Lewin’s theory to engage staff in the planning process, identify areas for improvement, and implement changes that resulted in enhanced patient care and staff satisfaction.
Effectiveness
Lewin’s Change Theory has proven effective in nursing practice due to its structured approach, focus on stakeholder involvement, and emphasis on creating a supportive environment for change.
- Structured approach:The three-stage model provides a clear roadmap for planning, implementing, and evaluating change, ensuring a systematic and evidence-based approach.
- Stakeholder involvement:Lewin’s theory emphasizes the importance of involving stakeholders throughout the change process. This fosters ownership, reduces resistance, and increases the likelihood of successful implementation.
- Supportive environment:The model encourages the creation of a supportive environment where individuals feel valued, respected, and empowered to embrace change. This reduces anxiety and resistance, promoting a positive attitude towards change.
Best Practices for Implementation

Implementing Lewin’s Change Theory in nursing requires careful planning and execution. Best practices encompass strategies for each stage of the change process: unfreezing, changing, and refreezing.
The following table Artikels best practices for implementing Lewin’s Change Theory in nursing:
Unfreezing Strategies
- Create a sense of urgency and need for change.
- Identify and address resistance to change.
- Develop a shared vision for the desired change.
- Build a coalition of support for the change.
Changing Strategies
- Communicate the change plan clearly and effectively.
- Provide opportunities for staff to learn and practice new skills.
- Monitor and evaluate the progress of the change.
- Make adjustments to the change plan as needed.
Refreezing Strategies, Lewin’s change theory in nursing ppt
- Reinforce the desired change through policies, procedures, and rewards.
- Celebrate successes and recognize staff contributions.
- Monitor the change over time to ensure it is sustained.
- Be prepared to address any resistance to the change that may arise.
Essential FAQs
What is the significance of unfreezing in Lewin’s Change Theory?
Unfreezing involves creating a sense of urgency and readiness for change. It requires nurses to identify and address the forces that maintain the status quo and encourage individuals to embrace new ideas.
How can nurses overcome resistance to change during the changing stage?
Nurses can overcome resistance by actively involving stakeholders in the change process, providing clear and compelling reasons for change, and offering support and resources to individuals affected by the change.
What are the key strategies for sustaining change during the refreezing stage?
Sustaining change requires reinforcing new behaviors and practices, evaluating progress, and making adjustments as needed. Nurses can use feedback, rewards, and recognition to encourage individuals to adopt and maintain the desired changes.