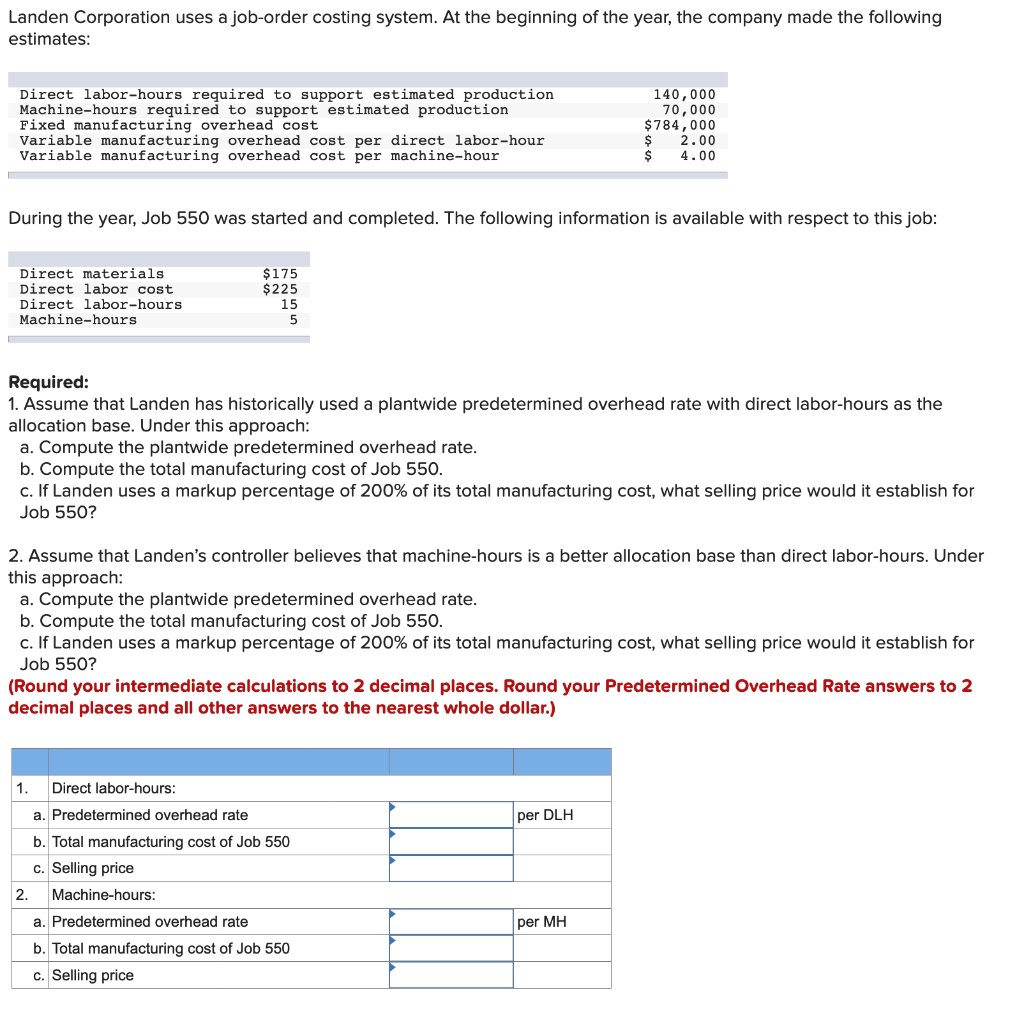
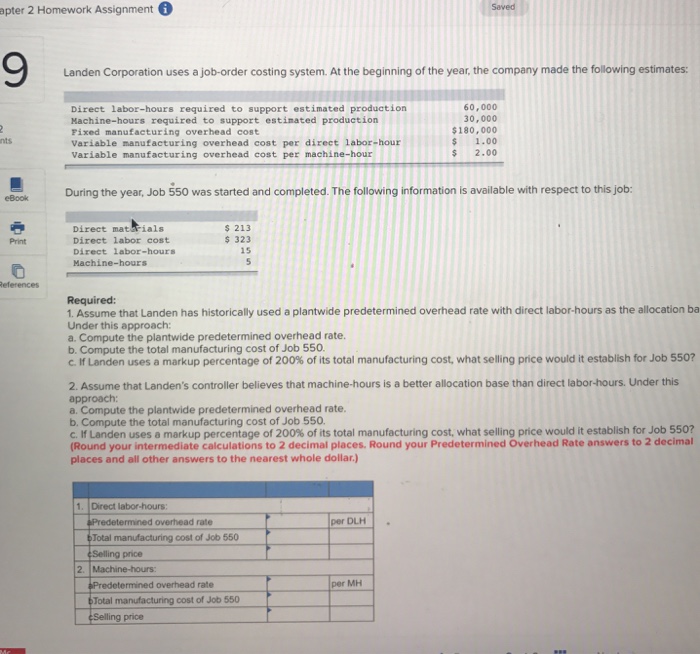
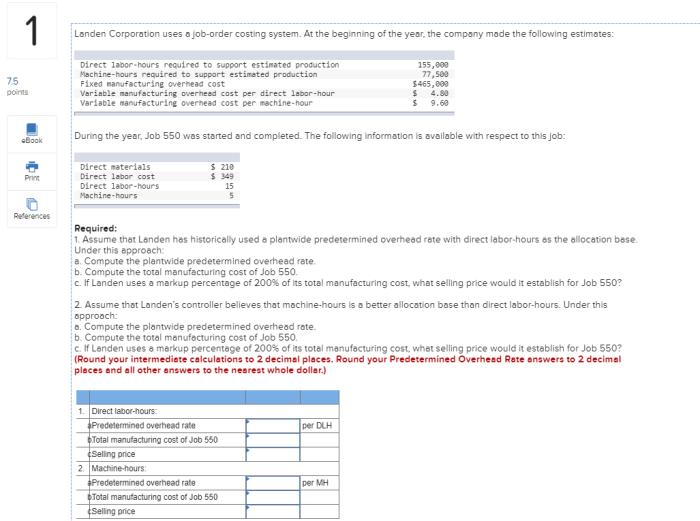
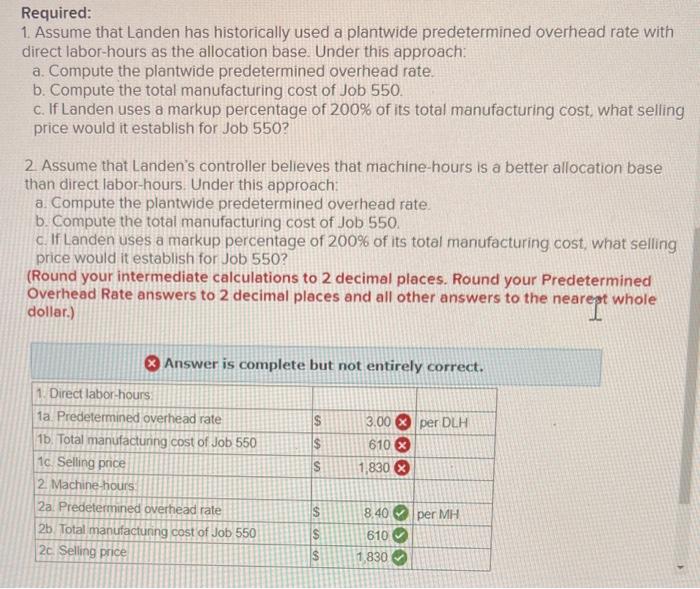
Landen corporation uses a job-order – LanDen Corporation’s adoption of a job-order costing system stands as a prime example of how this costing method can effectively manage complex operations in diverse industries. This in-depth exploration delves into the intricacies of LanDen’s job-order costing system, highlighting its advantages, challenges, and potential for improvement.
The job-order costing system plays a pivotal role in LanDen’s operations, enabling accurate cost allocation and providing valuable insights for decision-making. This analysis will shed light on the intricacies of LanDen’s costing process, examining its steps, advantages, and challenges.
Job-Order Costing System Overview
Job-order costing is a costing system that accumulates the costs associated with a specific job or production order. It is typically used in industries where products are produced in batches or on a one-off basis, and where the cost of each job needs to be tracked separately.
Examples of industries that typically use job-order costing include construction, printing, furniture making, and shipbuilding.
Characteristics of Job-Order Costing
- Costs are accumulated for each individual job.
- Jobs are unique and have different costs.
- Costs are assigned to jobs using direct labor, direct materials, and manufacturing overhead.
- Job cost sheets are used to track the costs of each job.
Advantages of Job-Order Costing
- Provides detailed cost information for each job.
- Helps to identify inefficiencies and areas for cost reduction.
- Supports decision-making by providing information about the profitability of each job.
Disadvantages of Job-Order Costing
- Can be time-consuming and expensive to implement.
- Requires a high level of accuracy in tracking costs.
- May not be suitable for industries with high-volume production.
LanDen Corporation’s Job-Order Costing System: Landen Corporation Uses A Job-order
LanDen Corporation uses a job-order costing system to accumulate the costs associated with each individual job or production order. This system is appropriate for companies that produce unique or customized products, as it allows for the tracking of costs specific to each job.
The steps involved in LanDen’s job-order costing process include:
Job Cost Sheet
When a new job is received, a job cost sheet is created to track the costs associated with that job. The job cost sheet includes information such as the job number, customer name, description of the job, and the estimated cost of the job.
Materials Requisition
When materials are needed for a job, a materials requisition is created. The materials requisition includes information such as the job number, the materials needed, and the quantity of materials needed. The materials requisition is then sent to the warehouse, where the materials are issued to the production department.
Time Ticket
When employees work on a job, they complete a time ticket. The time ticket includes information such as the job number, the employee’s name, the date, and the number of hours worked. The time ticket is then sent to the accounting department, where the employee’s wages are recorded.
Job Cost Report, Landen corporation uses a job-order
At the end of each month, a job cost report is created. The job cost report summarizes the costs associated with each job. The job cost report is used to determine the profitability of each job and to make decisions about pricing and production.
Advantages of Job-Order Costing for LanDen Corporation
LanDen Corporation benefits from using a job-order costing system in various ways. It enables accurate tracking of costs associated with specific customer orders, facilitating informed decision-making and efficient resource allocation.
Firstly, job-order costing provides detailed information about the costs incurred during the production of each job. This allows LanDen to determine the profitability of individual projects, identify areas for cost reduction, and optimize pricing strategies.
Enhanced Product Costing
Job-order costing helps LanDen accurately determine the cost of each product or service, considering direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead costs. This information is crucial for setting appropriate selling prices, ensuring profitability, and maintaining competitiveness in the market.
Improved Resource Management
By tracking costs at the job level, LanDen can effectively allocate resources and optimize production processes. The system helps identify inefficiencies, reduce waste, and improve overall operational efficiency.
Increased Customer Satisfaction
Job-order costing enables LanDen to respond promptly to customer inquiries regarding product costs and profitability. This transparency fosters trust and strengthens relationships with customers, leading to increased satisfaction and repeat business.
Facilitated Decision-Making
The detailed cost information provided by job-order costing supports informed decision-making at various levels of the organization. Managers can analyze cost data to make strategic choices about product mix, pricing, and resource allocation, ultimately enhancing the company’s overall performance.
Challenges of Job-Order Costing for LanDen Corporation
LanDen Corporation faces several challenges in using a job-order costing system, including the need for accurate cost allocation, the potential for errors in data collection, and the complexity of managing multiple jobs simultaneously.
To overcome these challenges, LanDen has implemented several strategies, including:
Accurate Cost Allocation
- Using detailed job cost sheets to track all costs associated with each job.
- Establishing clear guidelines for allocating indirect costs to jobs.
- Regularly reviewing and updating cost allocation methods to ensure accuracy.
Data Collection Errors
- Implementing a rigorous data collection process to minimize errors.
- Training employees on the importance of accurate data collection.
- Using technology to automate data collection and reduce the risk of human error.
Managing Multiple Jobs
- Establishing a clear job scheduling process to ensure that jobs are completed on time and within budget.
- Assigning dedicated project managers to each job to oversee its progress and manage its costs.
- Using project management software to track the status of each job and identify potential bottlenecks.
Alternatives to Job-Order Costing
LanDen Corporation can explore alternative costing methods to address the limitations of job-order costing. These methods offer different approaches to allocating costs and tracking production.
Process Costing
Process costing accumulates costs for a continuous or repetitive production process. Costs are averaged over the units produced during a specific period, resulting in a unit cost. This method is suitable for industries with standardized products and high production volumes.
Advantages:
- Simplified cost allocation for mass production
- Lower administrative costs compared to job-order costing
Disadvantages:
- Less accurate for products with significant variations
- Limited visibility into individual job costs
Activity-Based Costing (ABC)
ABC assigns costs to products or services based on the activities required to produce them. This method identifies cost drivers that consume resources and allocates costs accordingly.
Advantages:
- Improved cost accuracy by considering activity-based consumption
- Better understanding of cost structure and inefficiencies
Disadvantages:
- Complex and time-consuming to implement
- Requires detailed data on activities and cost drivers
Hybrid Costing
Hybrid costing combines elements of job-order costing and process costing. Costs are accumulated by job for unique or complex products, while standardized or repetitive processes are costed using process costing. This approach provides flexibility and accuracy.
Advantages:
- Customized costing for specialized products
- Simplified costing for standardized processes
Disadvantages:
- Increased complexity compared to pure costing methods
- Potential for errors in transitioning between costing systems
Recommendations for Improving LanDen’s Job-Order Costing System
To enhance the effectiveness and accuracy of LanDen’s job-order costing system, several recommendations can be implemented. These improvements aim to streamline processes, minimize errors, and provide more reliable cost information for decision-making.
Improved Data Collection and Entry
- Automate data collection processes to reduce manual entry errors and improve accuracy.
- Implement barcoding or RFID technology to track materials and labor usage, ensuring real-time data capture.
- Provide regular training to employees on proper data entry procedures to minimize mistakes.
Enhanced Cost Allocation Methods
- Explore alternative cost allocation methods, such as activity-based costing, to more accurately assign overhead costs to jobs.
- Consider using statistical sampling techniques to estimate overhead costs for improved efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Regular System Audits and Reviews
- Establish a regular schedule for system audits to identify and address any inefficiencies or errors.
- Conduct periodic reviews of cost estimates and actual costs to ensure accuracy and identify areas for improvement.
Potential Benefits of Implementing Recommendations
By implementing these recommendations, LanDen Corporation can expect several benefits, including:
- Increased accuracy and reliability of cost information for improved decision-making.
- Reduced errors and inefficiencies, leading to cost savings and improved profitability.
- Enhanced visibility and control over job costs, enabling better project management and resource allocation.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the primary advantage of using a job-order costing system for LanDen Corporation?
LanDen Corporation primarily benefits from job-order costing’s ability to accurately assign costs to specific jobs or projects, providing detailed insights into the profitability and resource allocation of each undertaking.
How does LanDen Corporation address the challenge of estimating overhead costs in its job-order costing system?
LanDen Corporation employs various methods to estimate overhead costs, including predetermined overhead rates based on historical data and industry benchmarks. This approach helps distribute overhead costs equitably across jobs.