The KHP + NaOH net ionic equation is a crucial aspect of understanding the chemical reaction between potassium hydrogen phthalate (KHP) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH). This equation provides insights into the behavior of ions in solution and has significant applications in various fields.
In this guide, we will delve into the details of this reaction, its net ionic equation, and its practical uses.
The balanced chemical equation for the reaction between KHP and NaOH is: KHP + NaOH → KNaP + H2O. This equation shows that KHP reacts with NaOH to form potassium sodium phthalate (KNaP) and water (H2O).
Introduction: Khp + Naoh Net Ionic Equation
In chemistry, a net ionic equation is a chemical equation that shows only the ions that are actually reacting. This is in contrast to a balanced equation, which shows all of the reactants and products, including those that are not actually involved in the reaction.
Net ionic equations are useful for understanding the true nature of a reaction and for predicting the products of a reaction. They can also be used to calculate the equilibrium constant for a reaction.
Potassium Hydrogen Phthalate (KHP), Khp + naoh net ionic equation
Potassium hydrogen phthalate (KHP) is a white, crystalline solid that is soluble in water. It is a weak acid with a pKa of 5.5.
Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH)
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is a white, crystalline solid that is soluble in water. It is a strong base with a pH of 14.
Reaction of KHP and NaOH

The reaction between potassium hydrogen phthalate (KHP) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is a classic acid-base titration reaction. This reaction is commonly used to standardize NaOH solutions in analytical chemistry.
Balanced Chemical Equation
The balanced chemical equation for the reaction between KHP and NaOH is as follows:
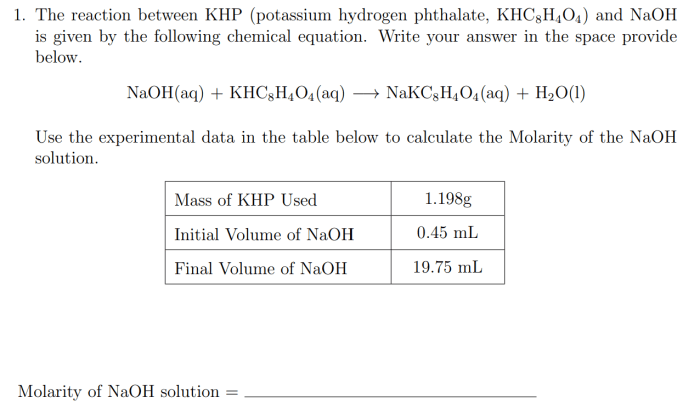
KHC8H 4O 4(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaKC 8H 4O 4(aq) + H 2O(l)
Reactants and Products
The reactants in this reaction are KHP and NaOH, while the products are sodium potassium phthalate (NaKC 8H 4O 4) and water (H 2O).
Type of Reaction
The reaction between KHP and NaOH is an acid-base reaction. In this type of reaction, an acid reacts with a base to form a salt and water. In this case, KHP acts as the acid, while NaOH acts as the base.
Net Ionic Equation

Concept of a Net Ionic Equation
A net ionic equation represents a chemical reaction by showing only the ions that participate in the reaction. It excludes spectator ions, which are ions that do not participate in the chemical change and are present on both sides of the equation.
Net Ionic Equation for KHP and NaOH
The net ionic equation for the reaction between KHP and NaOH is:“`H+(aq) + OH-(aq) → H2O(l)“`
Spectator Ions
In the reaction between KHP and NaOH, the spectator ions are K+ and CH3COO-. These ions are present on both sides of the equation and do not participate in the chemical change.
The net ionic equation for the reaction between KHP and NaOH is a classic example of a neutralization reaction. If you’re looking for some excitement in the field, check out our guide to the best chokes for quail hunting . With the right choke, you’ll be able to take down your target with ease.
But remember, the net ionic equation for KHP + NaOH is still a fundamental concept to grasp in chemistry.
Applications of the Reaction

The reaction between KHP and NaOH has various applications in different fields. Understanding the net ionic equation is crucial for comprehending the underlying principles and predicting the outcomes of these applications.
Uses in Analytical Chemistry
- Standardization of NaOH solutions:KHP is used as a primary standard to determine the exact concentration of NaOH solutions. The net ionic equation helps calculate the moles of NaOH accurately, enabling precise solution preparation.
- Acid-base titrations:The reaction is used in acid-base titrations to determine the concentration of unknown acids. The net ionic equation provides insights into the stoichiometry and equivalence point, ensuring accurate analysis.
Applications in Food Industry
- Leavening agent:KHP is used as a leavening agent in baking. When combined with NaOH, it releases carbon dioxide gas, causing baked goods to rise.
- Buffering agent:NaOH is used to neutralize acids in food products, maintaining a stable pH level. The net ionic equation helps predict the amount of NaOH required for effective buffering.
Other Applications
- Cleaning and disinfection:NaOH is used as a cleaning and disinfecting agent due to its alkaline properties. The net ionic equation provides information on the dissociation of NaOH, enabling effective dilution and usage.
- Textile industry:NaOH is used in textile processing to mercerize cotton fibers, giving them increased strength and luster. The net ionic equation helps optimize the NaOH concentration for effective mercerization.
Question Bank
What is the purpose of a net ionic equation?
A net ionic equation shows only the ions that participate in a chemical reaction, excluding spectator ions that do not change during the reaction.
What are the applications of the KHP + NaOH reaction?
The KHP + NaOH reaction is used in various applications, including acid-base titrations, buffer solutions, and the preparation of potassium salts.